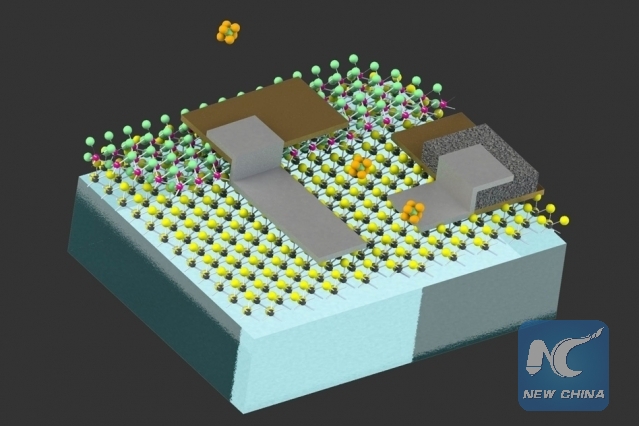
Diagram illustrates the design of the tiny devices, which are designed to be able to float freely in liquid or air. (Credit: MIT researchers)
SAN FRANCISCO, July 23 (Xinhua) -- Researchers at U.S. Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have created the world's smallest robots that can be used for medical diagnosis or industrial application such as detection of oil or gas leakage, a study said Monday.
According to the study published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, the tiny robots are devices about the size of a human egg cell, which consist of tiny electronic circuits made of two-dimensional materials, piggybacking on minuscule particles called colloids.
They are insoluble particles or molecules anywhere from a billionth to a millionth of a meter across, and they can stay afloat indefinitely in a liquid or in air.
The self-powered cell-size robots don't need any external power source or even internal batteries. Their circuits get the trickle of electricity from a photodiode to power their computation and memory circuits.
That's powerful enough for the tiny robots to sense information about their environment, store data in their memory, and make it possible to retrieve data upon mission completed.
MIT scientists hope their efforts can lay the groundwork for the tiny robotic devices to be used in the medical sector like the diagnosis in human digestive system, where they pass through the digestive tract searching for signs of inflammation or other disease indicators.
"Colloids can access environments and travel in ways that other materials can't," said Michael Strano, a professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT and a senior author of the study.
The researchers also want the tiny robots to be used for detection of oil or gas leakages in pipelines or waft through air to measure compounds inside a chemical processor or refinery.
In an industrial scenario, the robots can be inserted into one end of a pipeline and flow along toward the other end while checking for the presence of contaminants that indicate where potential problems are located.
Such devices could ultimately be a boon for the oil and gas industry, Strano said.

